
10 High Carb Foods That Are Surprisingly Healthy for You: A Guide to Healthy Carbohydrates
Understanding Carbohydrates: Debunking Common Myths About Carbohydrates
Recent years have seen a rise in the popularity of low-carb diets such as Atkins and ketogenic diets, which have given carbohydrates a bad reputation. A major aspect of these diets is the restriction of carbohydrates in order to lose weight and improve health markers such as blood sugar control and cholesterol levels.
It is important to note that not all carbohydrates are the same, and there are many high-carb foods that are incredibly healthy and extremely beneficial to our health as well as our overall well-being.
The key to a healthy diet is to differentiate between “good” and “bad” carbohydrates.
Weight Gain and Diabetes – Why Are Carbohydrates Blamed? Facts vs. fiction
A common association among people is that carbohydrates can lead to weight gain, type 2 diabetes, and other health conditions due to their ability to affect blood sugar levels.
When carbohydrates are consumed, our bodies convert them into glucose, which enters the bloodstream and raises blood sugar levels. As a result, the pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells, thereby regulating blood sugar levels.
Nonetheless, too much or the wrong type of carbohydrates (like those with a high glycemic index) can spike blood sugar levels and leave insulin levels elevated for a prolonged period. The result can be type 2 diabetes and other health problems caused by insulin resistance over time.
Refined sugars and processed grains are other high-carb foods that have a low nutrient content and are high in calories. Carbohydrates like these can contribute to weight gain, heart disease, and some types of cancer.
There are, however, many healthy and nutritious high-carb foods and many of these are actually very important for one’s overall health. Including complex carbohydrates in your diet, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, is crucial to maintaining a healthy blood sugar level, since these provide important nutrients and fiber.
10 Healthy High-Carb Foods for Optimal Health
QUINOA
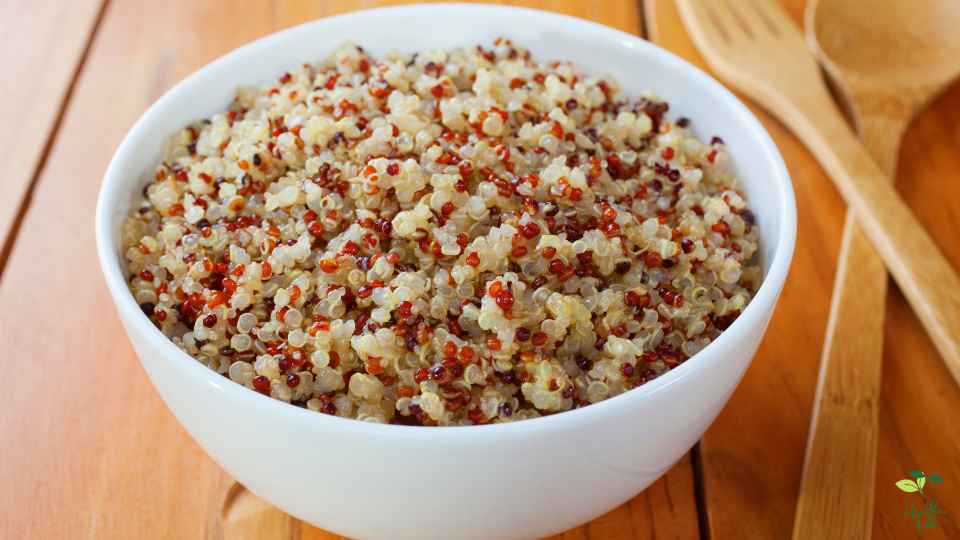

Nutritionally dense, quinoa has gained popularity as an alternative to traditional grains as a healthy food. While quinoa is often referred to as a grain, it is actually a seed that grows on the Chenopodium quinoa plant. Approximately 21% of quinoa’s dry weight consists of carbohydrates, which make up most of its carbohydrate content.
Quinoa is a great energy source due to its high carb content. Due to its complex carbohydrates, it provides sustained energy release since it is digested slowly. For athletes or people who require a steady stream of energy, quinoa is the perfect food.
Additionally, to carbohydrates, quinoa contains protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Especially high in iron, magnesium, and potassium, it is one of the most nutritious foods. Due to its high nutritional content and low glycemic index, quinoa is also a good food for controlling blood sugar levels.
As an added benefit, quinoa is gluten-free, making it a good alternative for people who have celiac disease or are sensitive to gluten. In addition to being versatile, quinoa can be used in a variety of dishes, such as salads, soups, and desserts.
The consumption of quinoa, as with all high-carb foods, should, however, be done in moderation as part of a balanced diet. In spite of the fact that carbohydrates are a vital source of energy, too much consumption can lead to weight gain and other health problems. In order to create a well-rounded meal, quinoa should be combined with vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
OATS
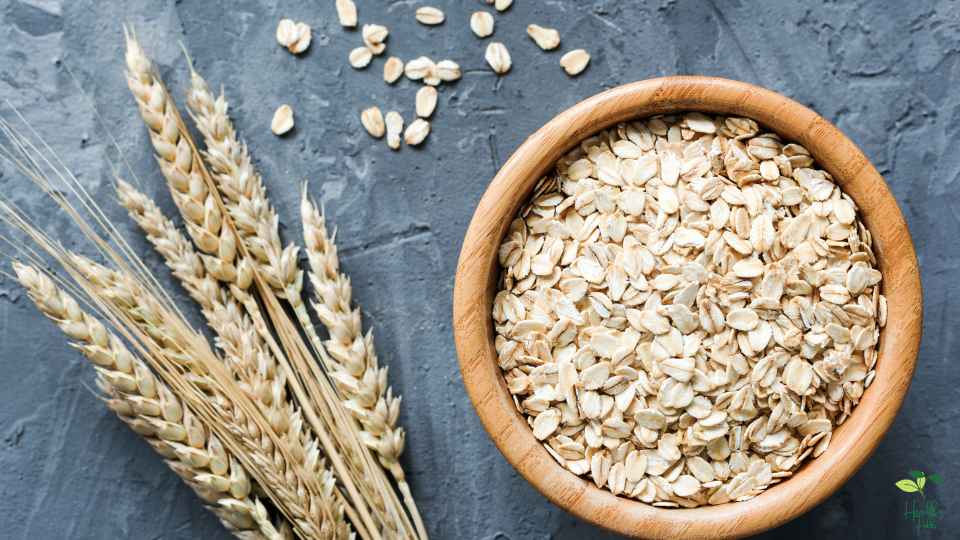

Oats are nutritionally dense whole grains that are rich in carbohydrates. An oat contains approximately 66% carbohydrates, making it a high-carbohydrate food. In contrast, the carbohydrates in oats are complex and are digested slowly by the body, so they supply sustained energy levels. Because of this, oats are a great food for athletes, those who live an active lifestyle, and anyone who needs a steady supply of energy throughout the day.
Furthermore, oats contain a lot of carbohydrates and amino acids, as well as fiber, vitamins, and minerals. One cup of cooked oats provides around 4 grams of fiber, making them high-fiber food. Because of oats’ high fiber content, they promote digestive health and prevent constipation.
Oats also contain beta-glucan, which is a unique type of fiber that lowers cholesterol levels and lowers heart disease risk. Those with diabetes may also benefit from beta-glucans ability to regulate blood sugar levels.
The versatile nature of oats makes them suitable for a variety of dishes, from oatmeal and baked goods to savory dishes such as meatloaf. Adding them to smoothies and dairy-free alternatives can give them a creamy texture.
Oats do not all have the same nutritional value, however. Choosing plain, unflavored oats are the best choice if you want to avoid added sugar and other additives. Moreover, oats, which are naturally gluten-free, can be contaminated by gluten when processed. If you are celiac or have gluten sensitivity, you should choose certified gluten-free oats.
BUCKWHEAT
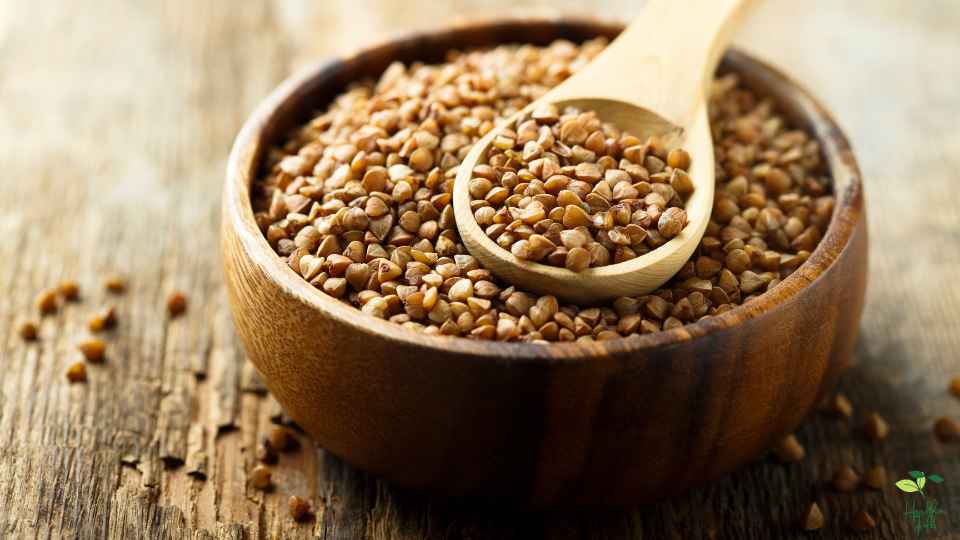

A high-carbohydrate diet often includes buckwheat, a highly nutritious pseudocereal. Besides being rich in complex carbohydrates and dietary fiber, it also contains several vitamins and minerals. Compared to other grains, buckwheat has a lower glycemic index, which means blood sugar levels don’t spike rapidly.
In one cup of cooked buckwheat, there are approximately 33 grams of carbohydrates, making it a good source of energy for dieters who need to keep their carbohydrate intake high. A cooked cup of this food contains only 155 calories, which makes it a low-fat and low-calorie food.
In addition to its high-quality protein content, buckwheat also contains essential amino acids when it comes to muscle growth and repair. Furthermore, it contains iron, magnesium, and manganese, which play important roles in keeping bones and muscles healthy.
A variety of dishes can be prepared with buckwheat, including porridge, pancakes, noodles, and even rice substitutes. A health-conscious population looking to include more whole, unprocessed foods in their diets has become increasingly interested in buckwheat due to its nutty taste and high nutritional content.
BANANAS

Bananas are a popular fruit high in carbohydrates that are often included in a balanced diet. Bananas are a good source of energy for those following a high-carbohydrate diet, as they contain approximately 27 grams of carbohydrates per medium banana.
Additionally, bananas contain dietary fiber, which helps reduce cholesterol levels and promotes healthy digestion. Besides vitamins and minerals, bananas contain potassium, manganese, and vitamin C.
As a potassium-rich food, bananas are particularly beneficial for regulating blood pressure and reducing the risk of heart disease. Furthermore, bananas contain antioxidants, which help prevent free radical damage to cells.
From smoothies and oatmeal to banana bread and snacks, bananas can also be incorporated into a variety of dishes and snacks. Several recipes can be created using them as a healthy ingredient or as a standalone fruit.
Generally, bananas are a nutritious, high-carbohydrate food that provides quick and easy energy along with improving overall health and well-being.
SWEET POTATOES

In high-carb diets, sweet potatoes are often included as a nutritious root vegetable. Complex carbohydrates, fiber, vitamins, and minerals make them an excellent source of energy and nutrients for people with high carbohydrate diets.
Approximately 23 grams of carbohydrates are found in one medium-sized sweet potato, making it an excellent source of energy. There are also many health benefits associated with eating sweet potatoes, including helping regulate digestion and reducing the risk of certain chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
Sweet potatoes are high in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin A, vitamin C, potassium, and manganese, in addition to carbs and fiber. While potassium is essential for maintaining heart and blood pressure health, vitamin A is particularly crucial for vision, immunity, and skin health.
Also, sweet potatoes provide anti-oxidants like beta-carotene that help shield cells from damage brought on by free radicals. Furthermore, beta-carotene has been associated with a lower risk of developing certain cancers, such as breast and lung cancer.
Soups, stews, casseroles, and even desserts may all be made using sweet potatoes, making them a very adaptable item. In many recipes, they work well as a healthier alternative to white potatoes by adding more nutrients.
As a whole, sweet potatoes are a high-carbohydrate, highly nutritive diet that can offer a variety of health advantages. They are a great supplement to any high-carb diet because they give you energy and important nutrients for your general health and well-being.
BEETS
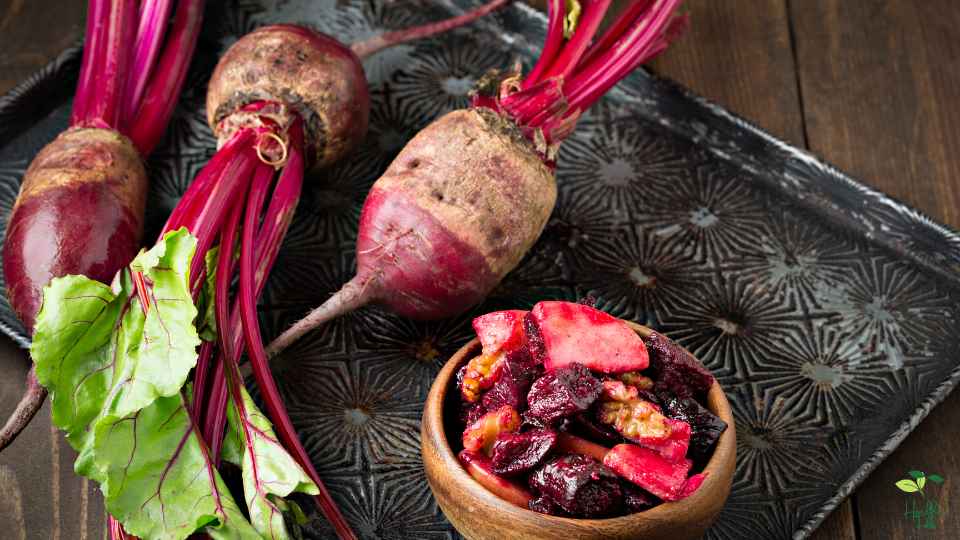
When compared to other vegetables, beets are said to have a fair amount of carbs. One cup (136 grams) of cooked beets has roughly 16 grams of carbs, according to the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA). Both natural sugars and complex carbs fall under this category.
The glycemic index (GI) of beets, on the other hand, is rather low, which means they don’t result in a sharp rise in blood sugar levels. This is because beets contain fiber, which slows down how quickly carbohydrates are absorbed and digested.
Despite not being a low-carb vegetable, beets can nevertheless be a part of a balanced and healthy diet for the majority of people. Beets are rich in nutrients and include essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that have a number of positive effects on health. A balanced consumption of carbs and other nutrients requires moderation and portion control, as with all foods.
ORANGES

Due to their high carbohydrate content per serving, oranges are regarded as having a high carbohydrate content. The amount of carbs in a medium-sized orange, which weighs about 154 grams, is about 17 grams. Glucose, fructose, and sucrose are just a few examples of the simple sugars that make up the majority of these carbs.
Oranges are not the fruit with the most carbohydrates, but they are nevertheless regarded as a rich source of fiber, vitamins, and minerals in addition to carbohydrates. Oranges are a terrific pre-workout snack because of their high carbohydrate content, which can be helpful for giving the body a rapid supply of energy.
The sugars found in oranges are natural sugars, which are typically seen as healthier than the added sugars present in many processed meals. However, those with specific health concerns, such as diabetes, may need to control their consumption of natural sugars and consume oranges in moderation.
DATES
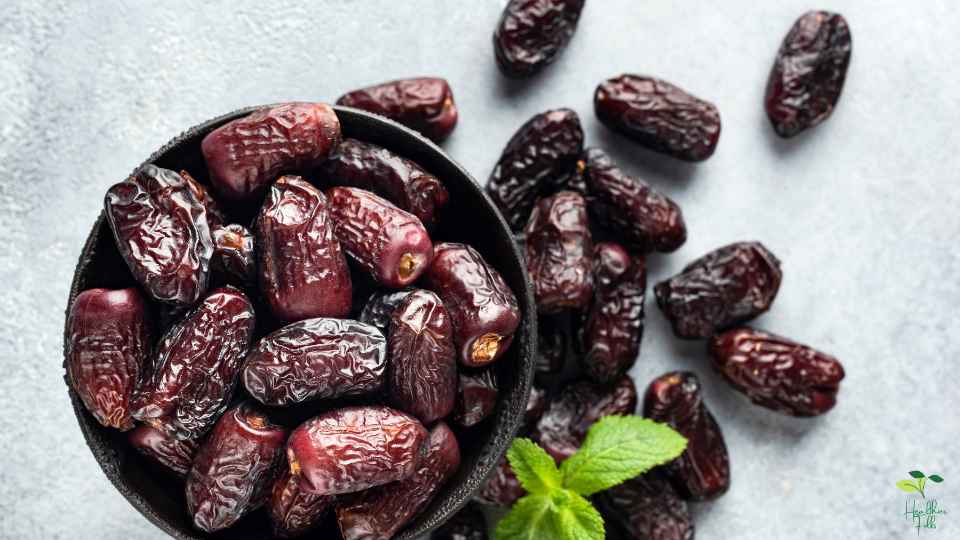

High-carb snacks such as dates are a natural source of carbohydrates. They are native to the Middle East and North Africa, where they grow on date palm trees. In many cuisines around the world, dates are popular due to their sweet and rich flavor.
Dates are rich in carbohydrates, containing about 66 grams of carbs per cup (about 5-6 dates), making them an excellent energy source. Sugars, such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose, make up the majority of carbohydrates in dates. Dates are a healthier alternative to processed and refined sugars found in many processed foods due to their natural sugar content.
The high carbohydrate content of dates is also complemented by the presence of fiber, which can contribute to feeling full after eating them. Aside from potassium, magnesium, and vitamin B6, they contain a variety of essential vitamins and minerals.
Dates are nutritionally beneficial, but they also contain a lot of calories, so they should be consumed in moderation. It is possible to gain weight and suffer other health problems if you consume too many dates or other high-carb foods. Choosing dates in a balanced diet is best when they are included alongside fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
GRAPEFRUITS
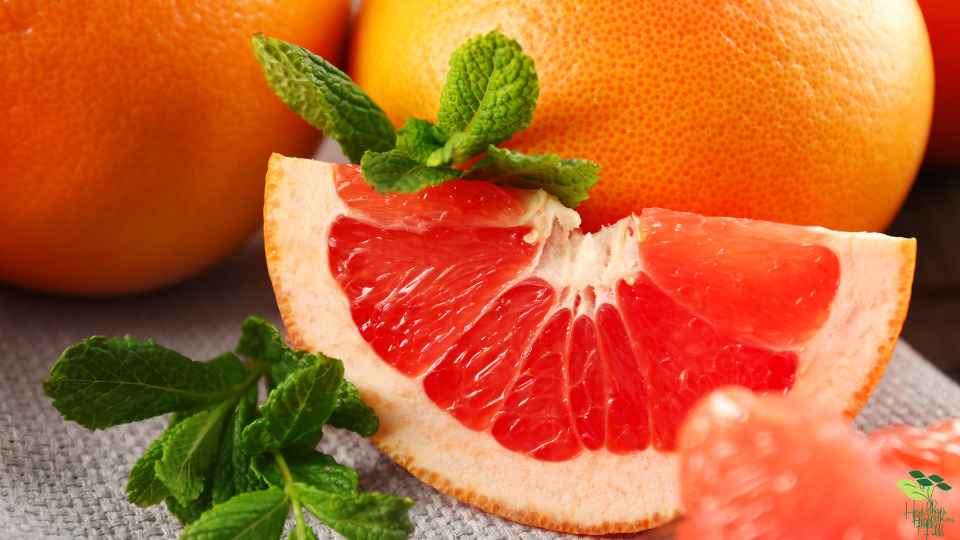

Grapefruits are nutritious fruits rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Furthermore, it contains only 8% carbs by weight, making it a relatively low-carbohydrate food.
In a medium-sized grapefruit half, there are approximately 11 grams of carbs, including 2 grams of fiber, bringing the net carb count down to 9 grams. The glycemic index of grapefruit is low, so it does not negatively impact blood sugar levels.
The carbohydrate content of grapefruit is complemented by the fact that just one-half of a medium-sized fruit supplies 70% of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C. Other essential vitamins and minerals, such as potassium, vitamin A, and folate, are also contained in smaller amounts.
Also, high in antioxidants, grapefruit contains lycopene and beta-carotene, which can help protect the body from oxidative stress and cellular damage.
Adding grapefruit to a balanced diet can be both healthy and nutritious. You should, however, consult with your healthcare provider before adding grapefruit to your diet if you take any prescription medications since grapefruit can interact with some medications, including cholesterol-lowering medications and antidepressants.
APPLES
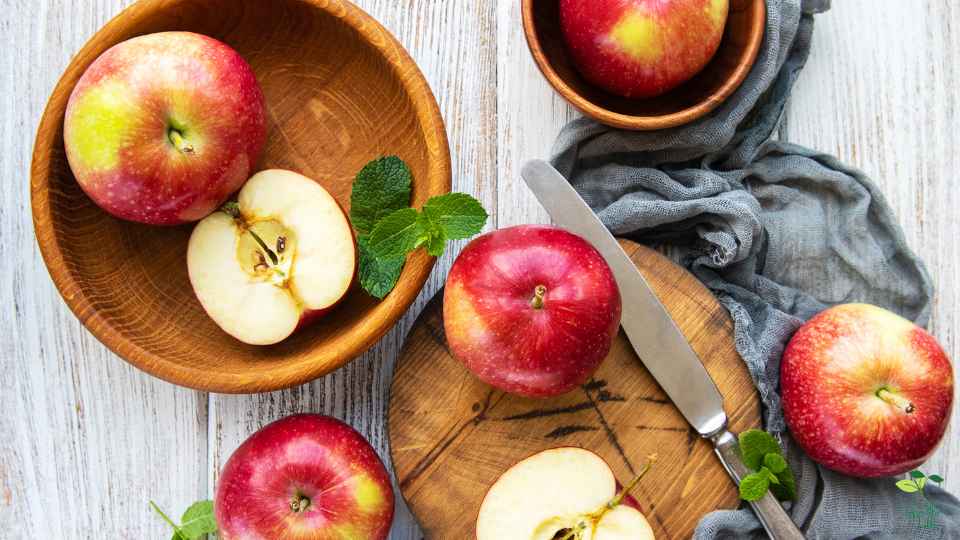

Around the world, apple products are popular and enjoyed by many people. Nutritionally, they are excellent and offer many health benefits. Carbohydrates are present in apples. There are approximately 19 grams of carbohydrates in one medium apple (approximately 182 grams), including 4 grams of fiber and 14 grams of sugar. Simple carbohydrates like fructose, glucose, and sucrose make up the majority of the carbohydrates in apples. Nevertheless, apples contain fiber, which reduces the absorption of these sugars, thus preventing blood sugar spikes. Despite their carb content, apples are regarded as a healthy and nutritious food that can be included in a balanced diet.
Additional information about apples’ nutrients is provided below:
- Vitamin C: About 14% of the daily recommended vitamin C intake is found in one medium-sized apple. This antioxidant supports a healthy immune system and helps protect cells from damage.
- Antioxidants: Antioxidants such as flavonoids and phenolic acids are abundant in apples. Inflammation and oxidative stress are both reduced by these compounds.
- Fiber: Besides soluble fiber, apples also contain insoluble fiber. By slowing digestion and lowering cholesterol levels, soluble fiber can help lower cholesterol levels. Insoluble fiber encourages regular bowel movements.
- Other vitamins and minerals: In addition to potassium and vitamin K, apples also contain vitamin B6 and vitamin K.
What do Healthierfolks want to say?
The overall benefits of adding apples to your diet include boosting your nutrient intake and improving your health.
Many of the healthiest foods contain a high percentage of carbohydrates, and it is not true that all carbohydrates are unhealthy.
The body requires carbohydrates, protein, and fat as macronutrients in order to function properly. Our bodies rely on carbohydrates for energy, and they are essential for maintaining brain function, muscle function, and other bodily functions.
There is, however, a difference between all carbohydrates. It is generally considered less healthy to consume simple carbohydrates like sugary drinks and processed foods, which can result in spikes in blood sugar levels. In contrast, complex carbohydrates are excellent sources of nutrients and fiber, providing sustained energy throughout the day.
To achieve optimal health and wellness, a balanced diet containing healthy carbohydrates, lean protein, and healthy fats is recommended.
Although not all carbohydrates are created equal, carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient that can be included in a balanced and healthy diet. Complex carbohydrates such as those found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables are highly nutritious, provide fiber, and provide sustained energy. The consumption of simple carbohydrates is recommended in moderation, including sweet drinks and processed foods. Overall health and well-being can be enhanced through a diet containing healthy carbs, lean protein, and healthy fats.



